CVSS score is commonly used in vulnerability management metrics by which the severity of vulnerabilities can be computed and compared.
CVSS scores range from 0-10, with this numeric rating being composed
of three sub groups of metrics (Base, Temporal, Environmental), of which
each metric group has several subcomponents.
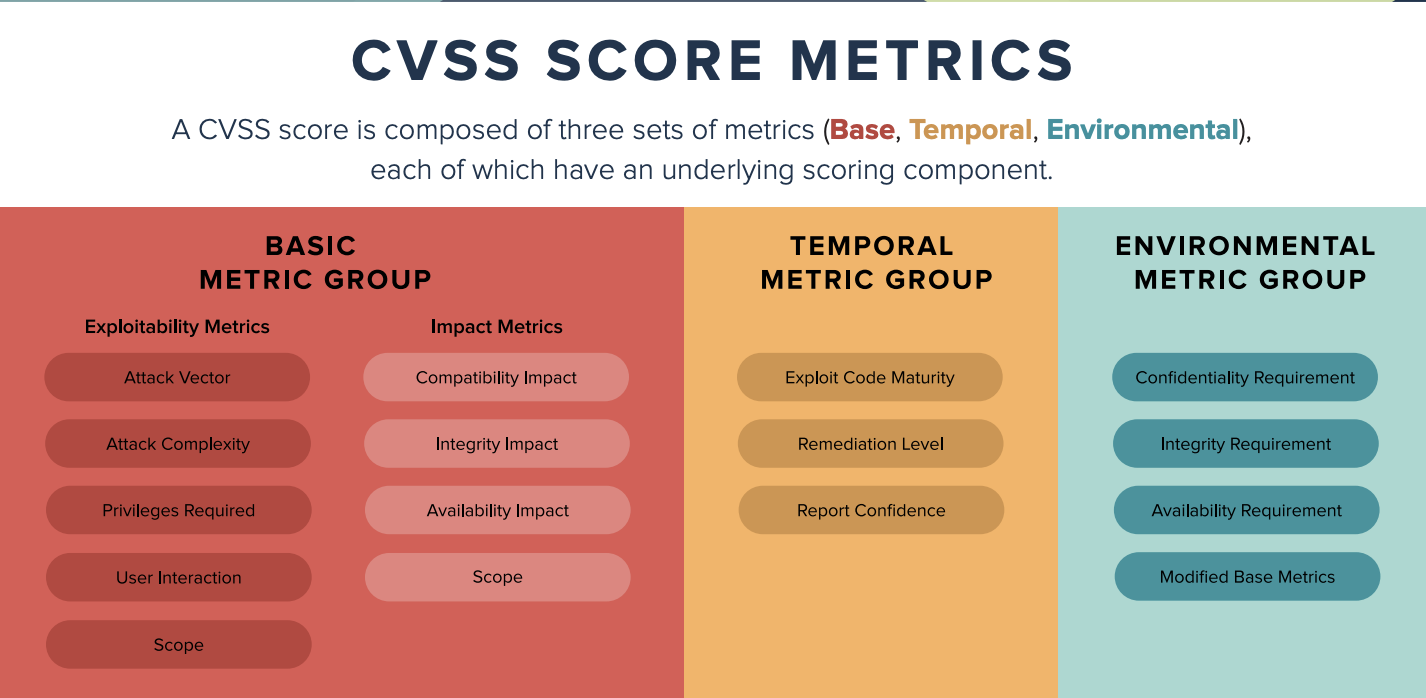 |
CVSS score metrics
|
Base metrics, which are the primary metric group reported in NIST's NVD. It is a public database of CVSS scores for known vulnerabilities. Base metrics do not cange over time, and remain the same throughout the lifetime of a CVE.
Temporal metrics, change over time as a result of activities conducted by both software vendors and hackers. These metrics may or may not be available in NVD. If the vendor has created a patch for public, the temporal score for the CVE will be lower. However, if there are known exploits for a vulnerability, the temporal score will be higher. As the availability of patches and exploit code changes, the underlying attributes of temporal metric will change including the overall CVSS score.
Environmental metrics apply to the specific environment in which a vulnerability exists. And it is specific to each enterprise. These metrics relate to either the business criticality of the asset, or to compensating controls that make an organization susceptible to the vulnerability.
CVSS Temporal Metrics
According to FIRST, “Temporal metrics measure the current state of exploit techniques or code availability, the existence of any patches or workarounds, or the confidence in the description of a vulnerability.” There are three metrics within this metric group – Exploit Code Maturity, Remediation Level, and Report Confidence.
Temporal Metric: Exploit Code Maturity/5
Exploit code maturity answers the question, “Is this exploit being used in the wild?” Many exploits are only theoretical in nature, and never actually get exploited by adversaries. Others get exploited, but code to operationalize those exploits never gets widely distributed, rendering it unusable to unskilled hackers, who represent the majority.
Exploit Code Maturity is rated at one of five levels: not defined (X), high (H), functional (F), proof-of-concept (P), unproven (U).
Temporal Metric: Remediation Level/5
Remediation level refers to the availability and maturity of a fix or patch for the vulnerability. As remediation code matures, the Temporal score will decreased.
Remediation Level is rated at one of five levels: not defined (X), unavailable (U), workaround (W), temporary fix (T), official fix (O).
Temporal Metric: Report Confidence/4
This metric measures the confidence level that the vulnerability actually exists, as well as the details of the issue. For example, if the vendor publicly acknowledges that a vulnerability exists, there is a very high confidence level that the vulnerability is real.
Report confidence is rated at one of four levels: not defined (X), confirmed (C), reasonable (R), unknown (U).
In order to calculate the overall CVSS score, beside getting the Base score, Temporal score must also be accounted for when determining the severity, and priority, of open vulnerabilities.
Links:









